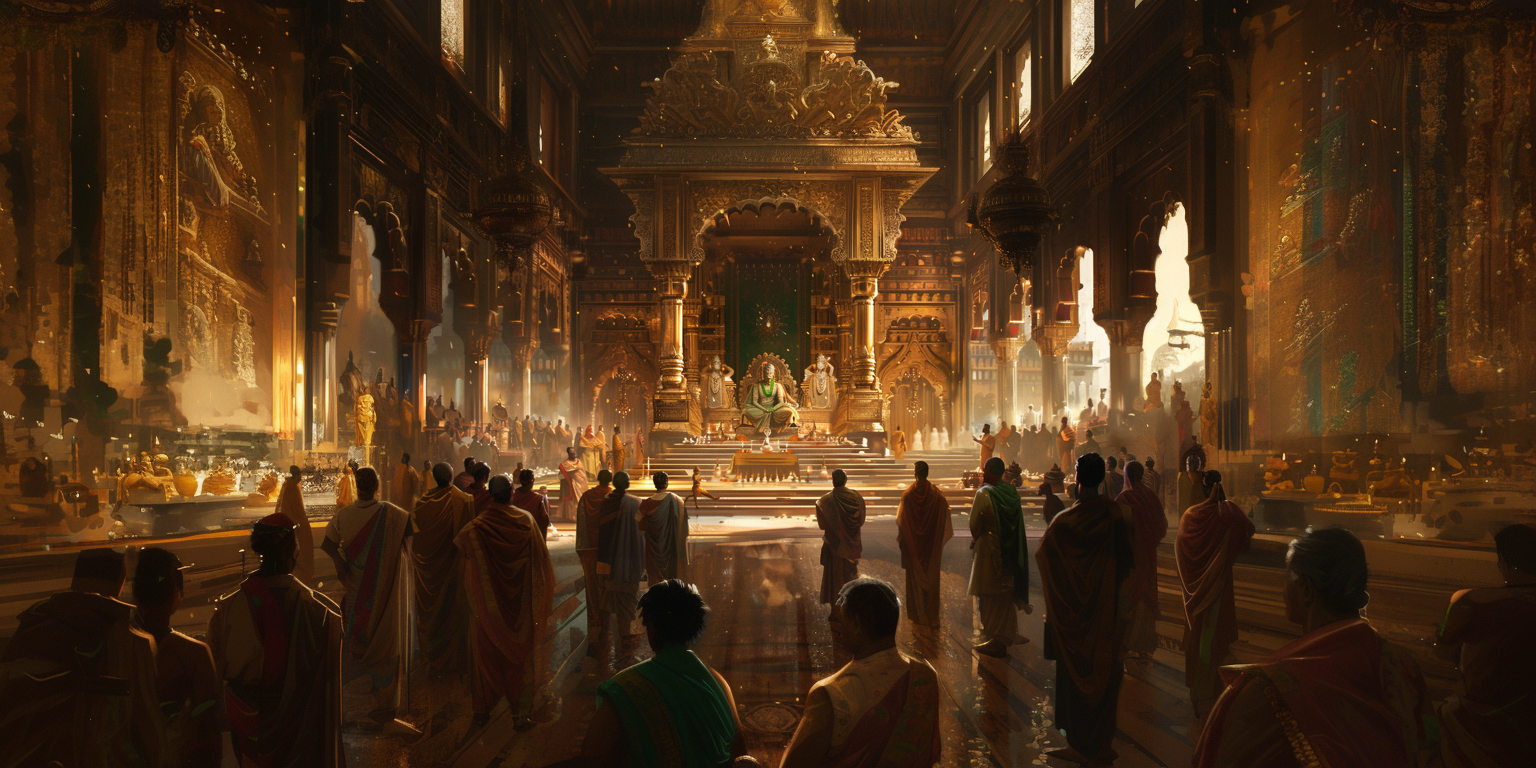
What catalyzed the rise of an intellectual and cultural revival in ancient India under the Gupta Empire?
Hailed as a golden age in the narrative of ancient Indian civilization, the Gupta Empire flourished around 300 CE. This time marked a distinct era of rapid advancements in varied domains such as the arts, literature, science, and philosophy. This era's cultural and intellectual accomplishments fascinate those exploring Indian Culture.
Exploring the foundation set by the intellectuals and the impact it created at a global level unveils insights into this transformative era. It sheds light on the innovative cultural and scientific progress of that time. Join me in uncovering these intellectual treasures of knowledge and their inspiration, which had an everlasting impact on Indian history.
The Intellectual Landscape of the Gupta Empire
Imagine the architectural marvels, poetic verses, and mathematical theorems you find captivating, all of which have roots in an empire flourishing over 1500 years ago. The Gupta Empire is often hailed as the golden age of Bharat, fostering exceptional intellectual feats. Groundbreaking achievements characterized this era as a golden age, but the processes of thought and the nurturing environment for these advancements remain fascinating.
The Gupta rulers excelled in governance and were champions of education and arts. Their era witnessed unprecedented advancements in various fields, including architecture, fine arts, science, and literature. Eminent figures in Indian history made significant contributions, impressing the nation and the global intellectual sphere. The rulers' endorsement of Hinduism, while supporting the growth of Buddhism and Jainism, added to the diverse fabric of Indian intellectualism.
Exploring the Gupta Empire's accomplishments allows us to appreciate a period marked by significant scholarly pursuits and innovations. Through this exploration into the intellectual scene of the Gupta Dynasty, we aim to identify the visionaries responsible for many advancements that still impact the world today.
Nine Gems of Bharat
In the Gupta Empire, the Navaratnas, or Nine Gems, are the scholars defining its scholarly court. These nine luminaries marked an era not just in Indian history but also in global intellectual history. Led by their intellectual curiosity and drive, they improved literature, scientific fields, and arts, leaving an indelible mark on their time. Their works have set an exceptionally high bar for the subsequent generations of scholars and artists.
Areas of Expertise of Nine Gems of India
| Scholar | Area of Expertise | Contributions |
|---|---|---|
| Kalidasa | Literature and Playwriting | Renowned works like "Shakuntala" and "Meghaduta" |
| Aryabhata | Astronomy and Mathematics | Authored "Aryabhatiya," which introduced the concept of zero |
| Varahamihira | Astronomy and Astrology | Wrote "Brihat Samhita" and contributions to horoscopy |
| Vishnu Sharma | Fables and Storytelling | Creator of "Panchatantra" |
| Amarasimha | Lexicography and Criticism | The compiler of "Amarakosha," a famous Sanskrit thesaurus |
| Dhanvantari | Medicine and Ayurveda | Known as the Father of Ayurveda |
| Shanku | Architecture and Engineering | Expert in Vastu Shastra (traditional Indian architecture) |
| Ghatakarpara | Poetry and Literature | Renowned poet content for romantic compositions |
| Kshapanaka | Rhetoric and Philosophy | Philosophical writings and contributions to rhetoric |
How does a Poet think?
Poetry is the language of the soul, an art form that has captivated hearts and minds for centuries. But have you ever wondered how a poet thinks? What goes on in their mind as they weave words into beautiful tapestries of emotion and imagery?
To understand a poet's thought process, one must delve into the depths of their creative mind. This realm is where imagination reigns supreme, where ideas float effortlessly like ethereal wisps. Poets are often deeply introspective, constantly observing and interpreting the world around them. They possess a unique ability to find beauty and meaning in the mundane, transforming ordinary experiences into extraordinary verse.
Drawing inspiration from nature, love, and the complexity of human emotions, poets possess an innate sense of observation. They see what others often overlook, unearthing the hidden treasures of life. Their thoughts are like cascades of poetry, flowing freely and uninhibited. They carefully choose each word and meticulously craft each line to capture the essence of their thoughts and emotions.
Kalidasa the timeless
Kalidasa represents the pinnacle of ancient Indian literature. His works, including Shakuntala and Meghaduta, best exemplify his mastery of classical Sanskrit literature and drama. These texts reveal a profound grasp of human emotions intertwined with vivid descriptions of nature.
His literature comprises a diverse range of poems and plays. His unique blend of lyricism and profound philosophy renders his works everlasting. Renowned for their beautiful descriptions of nature, various forms of love, and expressions of devotion, Kalidasa's pieces stand out. They are unmatched in their elegance and vibrant imagery within the Sanskrit literary and dramatic tradition.
What does a Mathematician think?
When we think of influential figures in Indian history, our minds often drift towards leaders, politicians, and conquerors. However, it is crucial to recognize the role of mathematicians in shaping our world. Mathematicians are not secluded in their realm of numbers and calculations; they are critical thinkers who analyze and solve complex problems. Their contributions extend far beyond the limits of equations and theorems.
Mathematicians have lent their genius minds to inspire and create in art and literature. Artists have used the Fibonacci sequence, a series of numbers that appear in nature, to create aesthetically pleasing compositions. Similarly, mathematicians have played a significant role in music, with the study of harmonics and frequencies leading to the development of musical scales and the understanding of acoustics.
A mathematician's thinking extends beyond numbers and calculations; it encompasses the ability to perceive patterns, solve complex problems, and provide insights into the world.
Aryabhata, a Pioneering Mathematician
Born in 476 CE, Aryabhata epitomized excellence in mathematics. His groundbreaking ideas transformed the landscape of problem-solving methodology. By harmonizing mathematical precision with empirical astronomical insights, Aryabhata earned accolades as a premier thinker in early astronomy.
Aryabhata's Aryabhatiya is a monumental work that illuminates arithmetic, algebra, and trigonometry. In it, he approximated the value of pi (π) with remarkable precision and introduced the revolutionary notion of zero as a numerical figure. Additionally, the treatise expounds upon strategies to resolve quadratic equations and endorses a heliocentric perspective of the cosmos.
Importance of understanding the root cause of a disease
Exploring the fundamental cause of diseases is a cornerstone of ancient Indian medicine. Ayurveda, deeply rooted in this philosophy, asserts that grasping the core issues facilitates more profound and durable remedies. Dhanvantari, a luminary in Ayurveda, is celebrated for his profound understanding and brilliant contributions to health care.
Dhanvantari, Icon of Ayurveda
Dhanvantari, hailed as the God of Ayurveda, significantly impacted the advancement of ancient Indian medicine. Regarded among the esteemed Nine Gems in the Gupta Empire, his insights substantially shaped Ayurvedic methodologies. He is said to have taught surgery to Sushrutha, who is known as the Father of Surgery. He stressed the comprehension of the body's doshas, laying the foundation for comprehensive health solutions. His legacy endures, enriching both physical and psychological well-being.
Treatments and Practices
Ayurvedic treatments, aligning with Dhanvantari's doctrine, seek to harmonize the doshas via custom interventions. These encompass dietary modifications, botanical remedies, and unique modalities like panchakarma. The thorough documentation of these ancient practices has enabled their integration into modern health regimens. Dhanvantari's initiation has been sustained over time, influencing current holistic healthcare immeasurably.
| Aspect | Dhanvantari's Contributions | Modern Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnosis | Emphasis on dosha balance | Customized health regimens |
| Treatments | Herbal and natural remedies | Integration into naturopathy |
| Therapies | Introduction of panchakarma | Adopted by holistic health centers |
Dhanvantari's wisdom underscores that addressing the disease's core mitigates it holistically, benefiting body, mind, and soul. This paradigm, set forth by ancient health authorities, offers profound teachings on contemporary health and well-being management, particularly in today's rapid lifestyle.
Varahamihira: The Astrologer and Astronomer
Varahamihira, a distinguished figure within the Gupta Empire's intellectual enclave, eloquently fused astrology and astronomy. His voluminous works and profound insights have unceasingly captivated minds across the ages.
Life and Times
Varahamihira's upbringing is deeply rooted in the admiration of the Sun under the tutelage of Adityadasa, his father. The tapestry of his life unfolded within the Gupta Empire's pinnacle, a time saturated with cultural vibrancy and intellectual progress. Surrounded by academia at the forefront of its era, Varahamihira's intellect found fertile ground.
Contributions
Among his vibrant contributions, "Pancha-Siddhantika" stands out as a beacon. In this treatise, he assimilated the astronomical wisdom from five preceding schools of thought, showcasing his profound understanding of the cosmos. Furthermore, he left an indelible mark on the tapestry of Indian astrology with his work "Brihat-Samhita." This magnum opus, a rich amalgamation of astrology, meteorology, and geography, was a guiding light for ancient astronomers and a stepping stone for future generations of astrologers and astronomers.
Amarasimha: The Proficient Critic
Amarasimha, among the revered Nine Gems of the Gupta Empire, is highly revered for his contributions to linguistics. Central to his legacy is the 'Amarakosha,' a foundational Sanskrit thesaurus. It serves as a cornerstone for scholars and learners exploring the Sanskrit language.
The 'Amarakosha' transcends simple word collections by meticulously structuring and classifying Sanskrit vocabulary. This structural organization is paramount for a nuanced understanding of the language's complexities. Amarasimha's innovation set his work apart, offering a comprehensive guide unmatched by his contemporaries.
His impact goes beyond the 'Amarakosha,' shaping the future of lexicography and broadening Sanskrit's study. By methodically categorizing words, he elevated the language's richness and facilitated its cultural and literary continuity. Amarasimha's Influence echoes through the ages, enriching scholarship and creative expression.
Vishnu Sharma: The Master Storyteller
Vishnu Sharma stands out for his seminal work in storytelling and education. His legacy as a master storyteller is undoubted, utilizing narratives to communicate life lessons and principles of governance. He revolutionized his era with pioneering teaching techniques. He understood the allure of stories as educational tools and, thus, penned the renowned Panchatantra. This collection of fables, steeped in Indian ethos, is praised for its entertaining value and profound philosophical messages. Sharma's stories effectively communicated complex moral and ethical teachings engagingly and memorably.
Panchatantra of Vishnu Sharma
Attributed to Vishnu Sharma, the Panchatantra is a timeless classic that crosses cultural and historical barriers. Its global Influence, with translations into numerous languages, shaped various literary traditions. Sharma strategically embedded practical leadership, strategy, and interpersonal conduct lessons in each fable. This strategic approach highlights the enduring relevance of his work and the depth of Sharma's educational impact.
Shanku: The Architectural Visionary
Shanku emerges as a significant luminary within the Nine Gems, his impact reverberating through the Gupta Empire's architectural endeavors. His pioneering approach and guiding architectural doctrines left an indelible mark on ancient Indian structural design.
Shanku's Architectural principles
During the Gupta era, Shanku significantly advanced the field of architecture. His seminal innovations laid the bedrock for India's distinguished classical architectural style. His methods revolutionized the creation and enhancement of both residential and governmental constructions.
The accent on symmetry and proportion was central to Shanku's architectural philosophy. He seamlessly weaved natural elements into his creations. These foundational principles defined the magnificence and elegance of Gupta-era buildings.
The following table delves into Shanku's fundamental architectural tenets and their respective uses across different architectural projects:
| Principle | Application | Notable Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Symmetry | Ensuring balanced and harmonious structures | Residential villas, state temples |
| Proportionality | Creating aesthetically pleasing and functionally efficient designs | City planning, public edifices |
| Integration of Natural Elements | Incorporating gardens, water features, and natural landscapes | Palatial complexes, regal parks |
Shanku's enduring Influence on ancient Indian architecture extends beyond tangible monuments from the Gupta period. It transcends into perennial principles, serving as a wellspring of inspiration for architects and builders worldwide.
Conclusion: The Legacy of the Gurukul Education System
The Gurukul education system, rooted in ancient India's Vedic traditions, was a key pillar for shaping highly accomplished individuals of its time. These illustrious figures, the Navaratnas, or the Nine Gems of India, thrived in an environment that combined the teachings of the Vedas with a focus on overall growth. As a result, they made extraordinary contributions to fields like literature, mathematics, astronomy, and medical science.
Nine Gems were products of a remarkable education system.
The Nine Gems' stellar achievements highlight the Gurukul system's efficacy. This method of education honed their critical and creative thinking skills, which were essential for their groundbreaking intellectual work—introducing students to a wide array of subjects and spiritual insights, sculpted polymaths. It equipped them to excel in diverse professional areas, leaving an indelible mark on the world's history.
The Gurukul system found its intellectual cornerstone in the Vedas. These ancient scriptures were not just religious texts but complex educational manuals. They encapsulated knowledge across disciplines that shaped the foundation of the ancient Indian educational philosophy. This tradition's profound impact reverberates today as scholars and educators globally find inspiration in its model. It highlights an enduring commitment to learning, discipline, and the relentless pursuit of wisdom.